Inflammation and gut health are two concepts that have garnered increasing attention in recent years, particularly due to their interconnectedness. The gut, often referred to as the “second brain,” plays a crucial role in regulating our overall health, including inflammation levels in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with a variety of health issues, including autoimmune diseases, digestive disorders, and even mental health conditions. This article explores the link between inflammation and gut health and how gut cleansing may help reduce inflammation.
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is a natural immune response to injury or infection. When the body detects a threat, such as a pathogen or a damaged cell, it releases inflammatory molecules that promote healing. In this acute phase, inflammation is beneficial and necessary. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can contribute to the development of various diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, arthritis, and neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s.
Chronic inflammation often arises from factors such as poor diet, stress, lack of exercise, environmental toxins, and an imbalance in gut microbiota. The gut is home to trillions of bacteria and microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome, which play a significant role in maintaining immune balance and regulating inflammation.
The Role of the Gut in Inflammation
The gut is directly linked to the immune system. In fact, about 70% of the body’s immune cells reside in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). This means that an imbalance in the gut microbiome, often caused by poor diet, antibiotics, or other factors, can lead to immune dysfunction and inflammation.
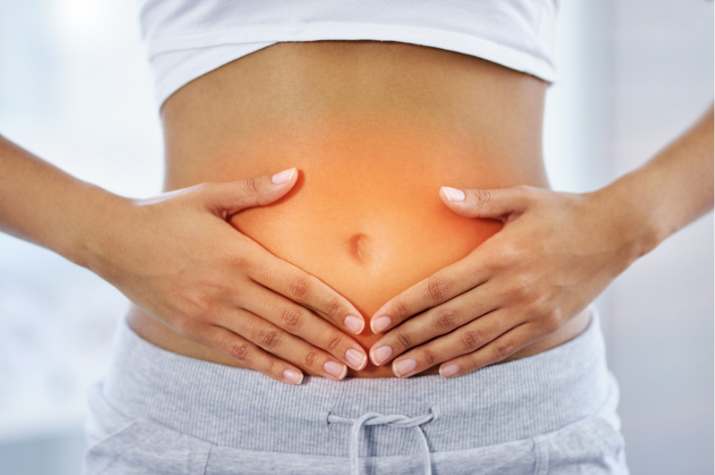
An unhealthy gut may contribute to “leaky gut” syndrome, a condition where the intestinal lining becomes damaged, allowing harmful particles such as toxins and bacteria to enter the bloodstream. This can trigger an immune response, leading to systemic inflammation and increasing the risk of chronic conditions.
Moreover, an imbalanced gut microbiome, often marked by an overgrowth of harmful bacteria and a lack of beneficial ones, can exacerbate inflammation. When these harmful microbes dominate, they produce compounds that promote inflammation, further compounding the issue.
Gut Cleanse: A Potential Solution for Inflammation
A gut cleanse typically refers to a process designed to reset the digestive system by eliminating toxins, improving gut flora, and enhancing digestion. While the concept of cleansing has been around for centuries in various cultures, it has gained modern popularity due to its potential to improve overall health, including reducing inflammation.
A gut cleanse may involve dietary changes, fasting, or the use of supplements such as probiotics, prebiotics, and herbal remedies that support detoxification and the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
How a Gut Cleanse Can Help Reduce Inflammation:
- Restoring Gut Flora Balance: A healthy gut microbiome is essential for controlling inflammation. Probiotics and prebiotics found in certain foods or supplements can help replenish beneficial bacteria, which can, in turn, reduce inflammation. Beneficial bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that help maintain a healthy gut lining, reducing the likelihood of leaky gut and chronic inflammation.
- Reducing Gut Permeability (Leaky Gut): By removing processed foods, sugars, and inflammatory foods from the diet, a gut cleanse can help reduce the damage to the intestinal lining and restore its integrity. This can minimize the risk of toxins and bacteria entering the bloodstream and triggering systemic inflammation.
- Eliminating Toxins and Harmful Substances: A cleanse can help remove accumulated toxins from the gut, liver, and other organs, preventing these substances from causing oxidative stress and promoting inflammation. Certain herbs and detoxifying foods, such as ginger, turmeric, and dandelion root, have anti-inflammatory properties that can support the detox process.
- Improving Digestion and Absorption: Poor digestion can lead to an overload of undigested food particles in the gut, which may provoke an immune response and cause inflammation. A gut cleanse can improve digestion, ensuring that nutrients are absorbed efficiently while reducing the likelihood of digestive disturbances that can lead to inflammation.
- Supporting Immune Function: Since the gut is integral to immune health, a balanced microbiome can help regulate immune responses. A healthy gut reduces the likelihood of inappropriate immune reactions that lead to chronic inflammation.
Foods That Support Gut Health and Reduce Inflammation
Incorporating anti-inflammatory and gut-friendly foods into the diet can further support the effectiveness of gut cleansing:
- Fermented Foods: Yogurt, Kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha are rich in probiotics, which support the growth of healthy gut bacteria.
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes are high in fiber, which serves as a food source for beneficial gut bacteria and promotes gut motility.
- Anti-Inflammatory Herbs and Spices: Turmeric, ginger, garlic, and cinnamon have potent anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce gut inflammation.
- Bone Broth: Bone broth contains collagen and gelatin, which can support the gut lining and promote digestive health.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Fatty fishlike salmon, chia seeds, and walnuts are rich in omega-3s, which have powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
Conclusion
The link between inflammation and gut health is undeniable, and addressing gut imbalances can be a key strategy for managing chronic inflammation. A gut cleanse that restores the balance of the gut microbiome, reduces gut permeability, and eliminates toxins may provide significant benefits for reducing inflammation and improving overall health. However, it is important to approach any gut cleanse with caution and ideally under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as each person’s body is unique and may require different interventions. By prioritizing gut health through diet, lifestyle, and occasional cleansing, individuals can enhance their immune function and reduce the risk of chronic inflammatory diseases.